You cannot learn or do Celestial Navigation without it. ABC and Sight Reduction Tables.
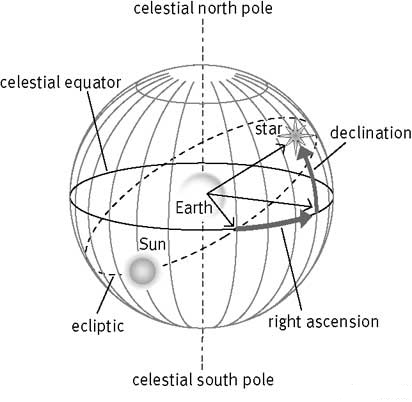
In celestial navigation this point is called the vernal equinox which is the Spring time intersection of the celestial equator the Earths equator projected outwards on the celestial sphere and the ecliptic plane the path the Earth takes around the Sun a k a the summer solstice if you are in the Northern Hemisphere.

. Difference of altitude true altitude computed altitude. Using an horary quadrant to find time of day by measuring the Suns altitude. A horary quadrant is used to find the time of day by measuring the Suns altitude.
Nav time diagram. A Short Guide to Celestial Navigation CELEBRATING 24 YEARS Henning Umlands Homepage. Obtaining a Position Line.
National Museum of American History Smithsonian Institution. Make sure proper DR was used for time of event. Z is the zenith which happens to be the Celestial Equator.
This is especially important in star sights as you only have the short time between civil and nautical twilight when the horizon is still visible while some stars are bright enough to be seen. Knowledge of the positions of celestial bodies with respect to time. It is a comprehensive illustration of the relationship between hour angles and meridian angles on the cele.
Using a mariners astrolabe to measure the angle of the Sun or a star above the horizontal. Deciding what celestial body you are going to shoot and when. But you NEED it.
A scientific calculator is extremely helpful in solving trigonometry. 11 N ovember 2004 James A. So the Diagram on the Plane of the Meridian is easy to draw.
CELESTIAL NAVIGATION TUTORIAL. Chapter 1 The Basics of Celestial Navigation Celestial navigation a branch of applied astronomy is the art and science of finding ones geographic position through astronomical observations particularly by measuring altitudes of celestial bodies sun moon planets or stars. A time diagram is a diagram on the plane of the celestial equator or equinoctial in which the celestial equator appears as a circle and celestial meridians and hour circles as radial lines.
30 045 30 026 19. Civil and nautical twilight time are found in the Almanac. Point of aries star sun.
We solve the formulae of celestial navigation calculating computed estimated Altitude and Azimuth using Altitude - Azimuth worksheet. An observer watching the night sky without knowing anything about. Celestial navigation 2014 pdf Chia-Yi Yen.
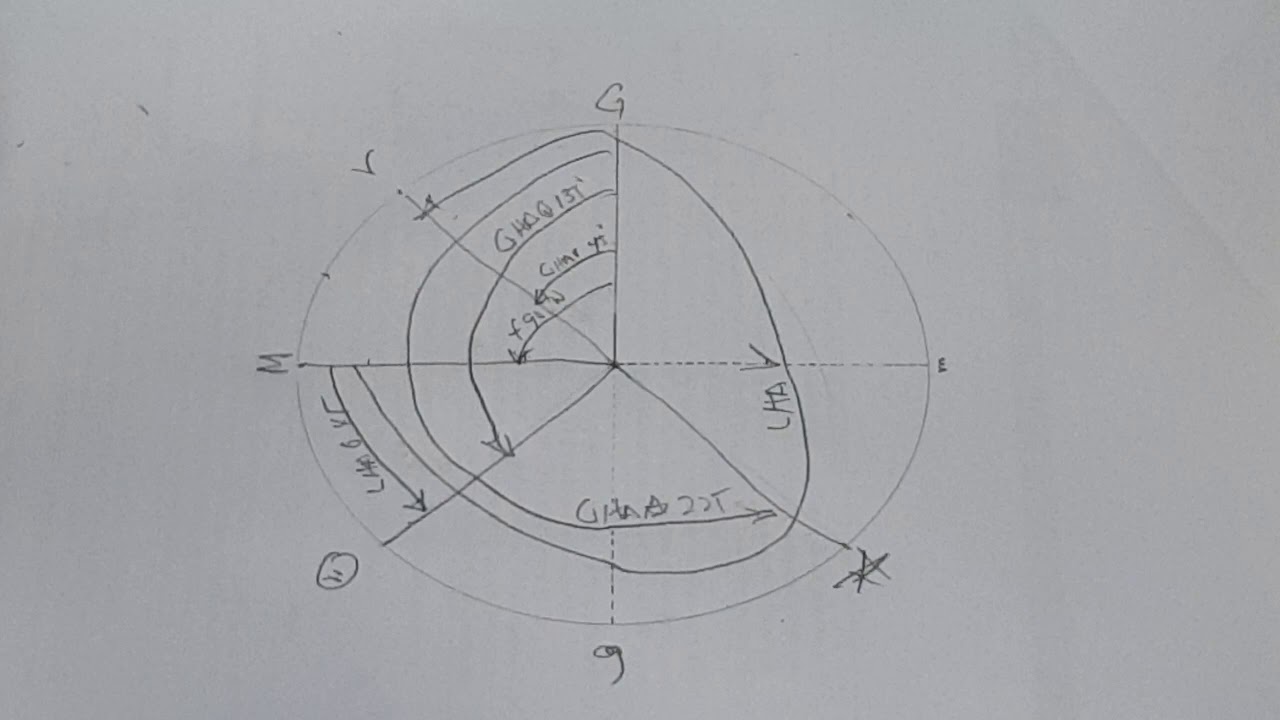
DeÞnition of the zenith distance of a star or other celestial object. Computation of LHA of Aries for Star Time. Lha gha sha ra lmt gmt.
Position Lines 3. I created this video to simplify the Time Diagram. Rotating the diagram make it easier to visualize the local sky at the equator.
Precise measurement of the time of observation. The celestial sphere the coordinates system seasons phases of the moon and eclipses. My intention is for this book to be used as a self-teaching tool for those who have the desire to learn celestial from the natural academic and practical points of view.
Calculating the Bearing and Distance. Visitors since May 20 1997. The dashed line points down directly from the Navigator to the nadir which happens.
MT Celestial Navigation Project --- Sea Term 2017 4 Practice. But for you to actually go out and practice on your own as well as learning the anatomy of the almanac you will want your own up-to-date copy. It is the average time between two consecutive passes of the Sun through the meridian.
Correcting a Sextant Altitude. V an A llen 1419. Nautical Almanac Software Plotting Tools Books more.
The reference used in marine navigation is the visible horizon. Hour angles and aries lrg. Celestial Navigation in the GPS Age by John Karl and of course the USPS Junior Navigation and Navigation manuals past pre 2006 and present editions et al.
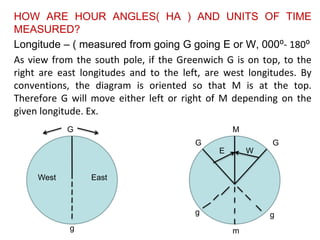
Diagram of angles between Polaris an observer and the earth. Computation of Star Time. It is used to facilitate solution of time problems and other problems involving arcs of the celestial equator or angles at the pole.
It is on average 24. The meridian passage of a celestial body is the time where it is at its highest point in the sky according to an observer. Using a Sextant Altitude 2.
Celestial navigation is a scientific art form that uses the sun moon stars and planets for navigating across the surface of the earth. October 9 th 2019. And half way between Sunset and Civil Twilight in the PM.
Solar day relative to the Sun. N and S mark the intersections of the North and South points of the horizon which just happen to be the Poles with the celestial meridian. Sight Calculations and Obtaining a Position 6.
Time zones and international date line idl. Angular measurements altitudes between the celestial body and a known reference. Use second estimate if necessary Star time is half way between Nautical and Civil Twilight in the AM.
Torial diagram S represents the intersection of the meridian plane through a star or any other celestial object with the equator. The tutorials in this book are for the summer of 2005 and all the almanac pages youll need to follow along are provided.
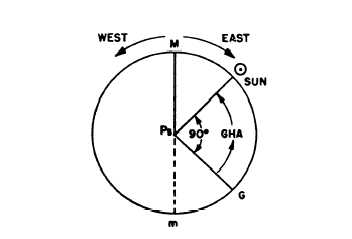
Figure 15 6 Time Diagram 14070 346

Celestial Navigation Demystified Time Diagram Youtube

Celestial Navigation Demystified Time Diagram Youtube


0 comments
Post a Comment